BHFUSE PPTC in Robotics Applications
Robots typically possess the following characteristics, making PPTC an ideal protective component:
Extreme Dynamic Loads: The joint motors of robots frequently start, stop, reverse, and withstand sudden load changes, generating huge inrush currents and back EMF, which can easily lead to overcurrent.
High Value and High Reliability Requirements: The robot itself and the tasks it performs are of high value; unexpected downtime can cause significant losses. PPTC can prevent production interruptions caused by minor faults and automatically recover after fault elimination, requiring no manual intervention.
Dense Electronic Systems: Centralized main control boards, sensors, servo drivers, etc., create a highly integrated system where a fault in one sub-unit can cause a chain reaction. PPTC enable fault isolation.
Stringent Safety Standards: Especially for collaborative robots, strict functional safety standards (such as ISO 13849) must be followed, requiring comprehensive fault protection mechanisms.
Harsh Environments: Vibration, dust, and temperature variations in industrial environments increase the risk of short circuits and overcurrent.
Three Major Application Scenarios for PPTC in Robotics
PPTC protect three core modules in robotic systems: the power execution system, the perception control system, and the human-robot interaction system.
1. Power and Execution System
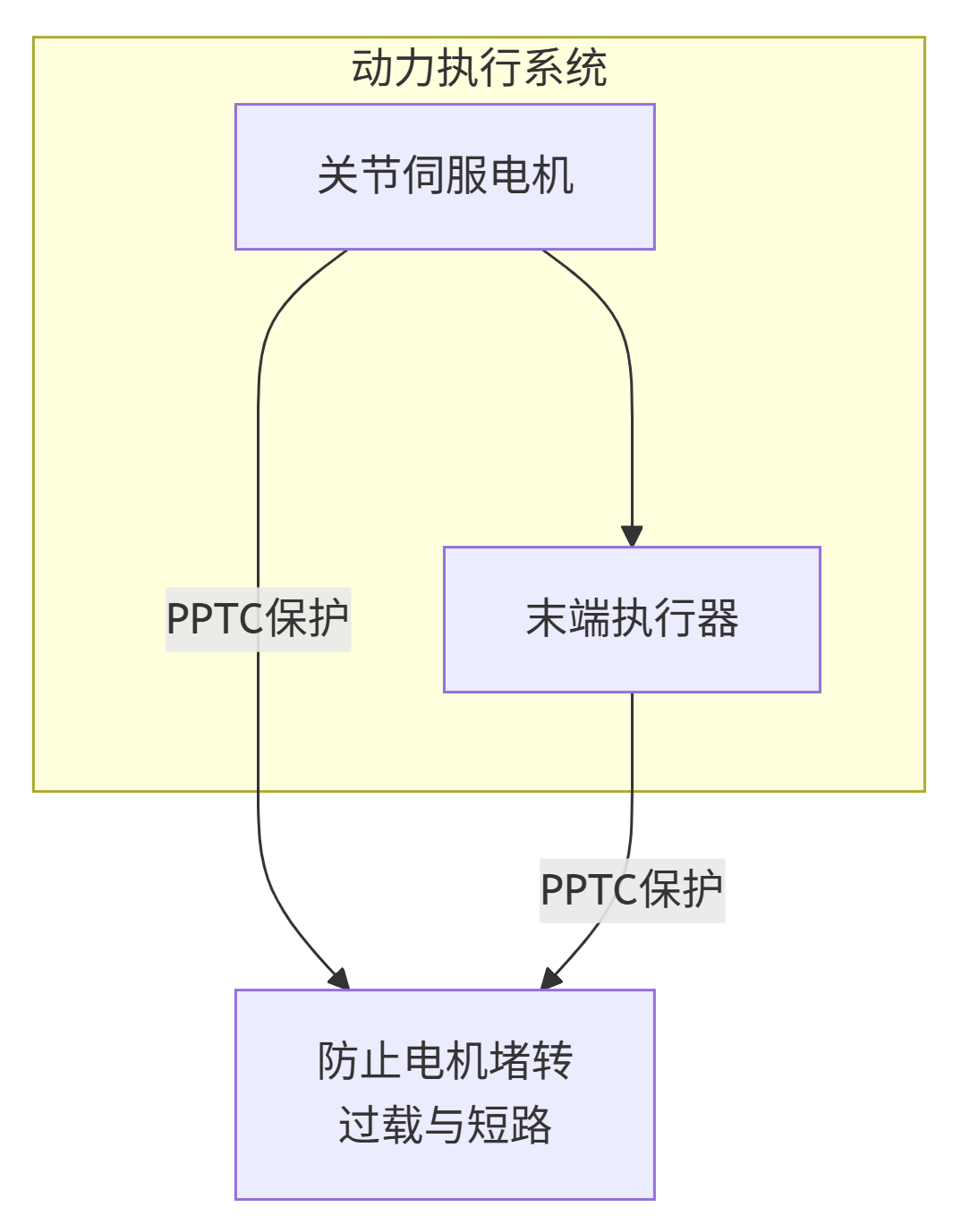
This is the area with the highest current and the most prone to failures in robots, making it a core application scenario for PPTC.
Joint Servo Motors/Actuators:
Risk: Risk: If a robot's joint suddenly jams during operation (stall condition), the current can instantly surge to 5-10 times the rated value, making it highly prone to burning out expensive motors or driver chips within seconds.
PPTC Role: Responds quickly by entering a high-resistance state, limiting the current, acting like a "pause button" for the motor. After the jam is cleared, the PPTC cools and recovers, allowing the robot to attempt to resume operation or safely report an error, preventing permanent hardware damage.
End Effectors:
Such as electric grippers, welding torches, glue dispensing valves, etc. PPTC are similarly used to prevent their drive motors from burning out due to jamming or overload.
Main Power Distribution Circuits:
PPTC are used at the power input or on power branches of various subsystems as secondary protection to prevent total system power failure due to internal short circuits.
2. Perception and Control System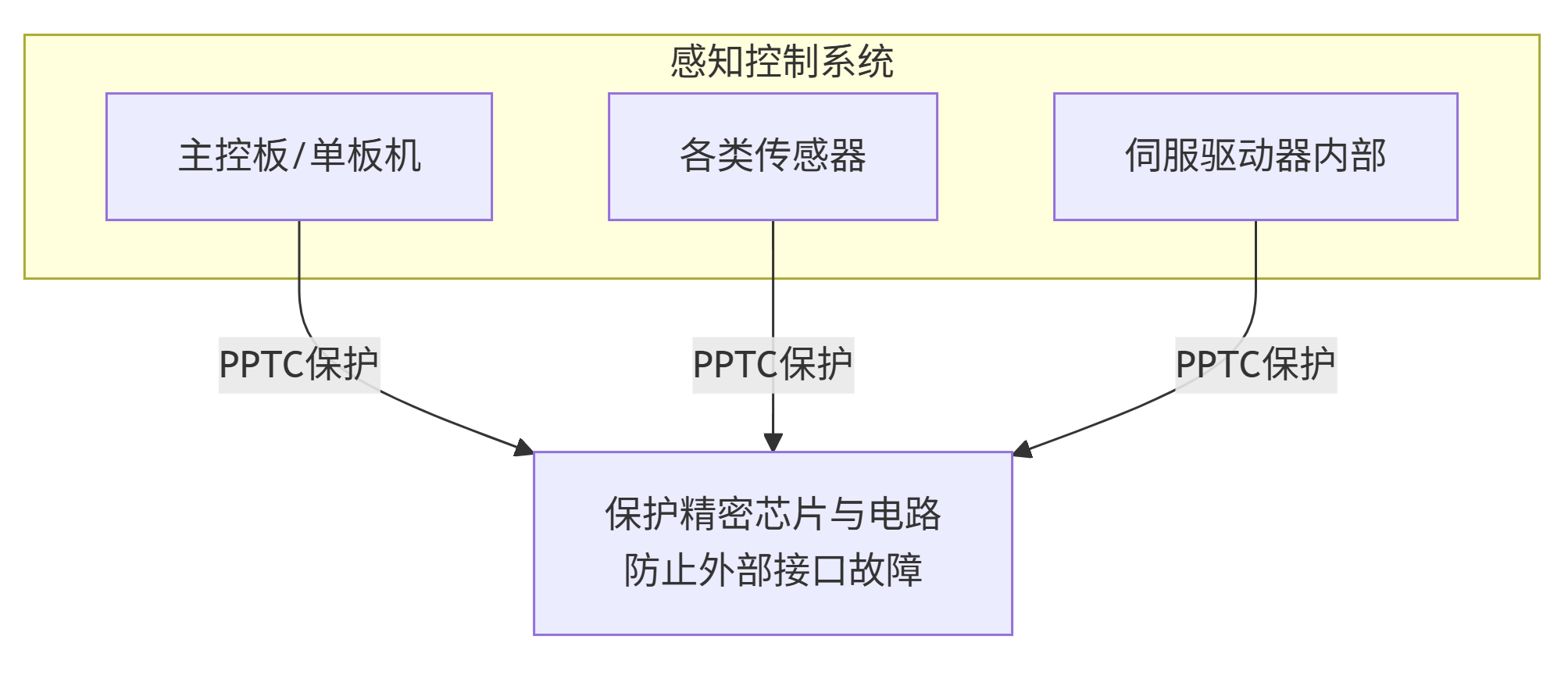
This is the "brain" and "nerves" of the robot – precise and fragile.
Main Control Board: Protects the power supply for the core processor, memory, and peripheral interfaces like USB and Ethernet, preventing the entire "brain" from being paralyzed due to peripheral faults.
Sensor Array:
LiDAR, Vision Cameras: These expensive sensors are connected via cables. PPTC can protect their power lines from damage caused by wear-induced short circuits or hot-plug surges.
IMU, Force/Torque Sensors: PPTC provide detailed overcurrent protection for these precision devices.
Inside Servo Drivers: Protects the low-voltage control logic circuits and encoder feedback circuits of the driver, ensuring the control system can still shut down safely and report errors even if the power section is abnormal.
3. Human-Robot Interaction and Safety System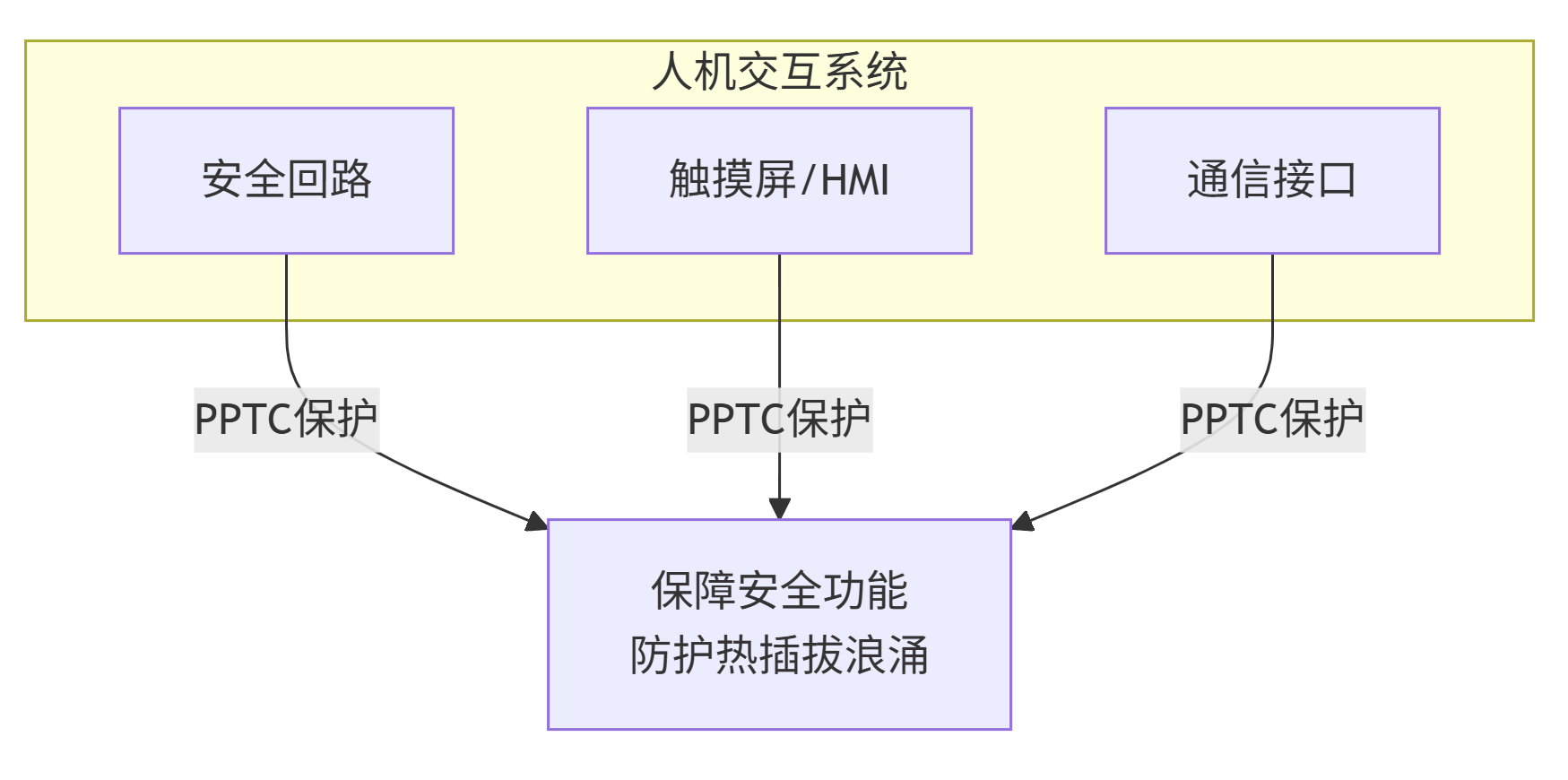
Safety Loops: In some non-critical safety monitoring circuits, PPTC can ensure that the monitoring circuit itself does not fail due to overcurrent, guaranteeing its continuous operation.
Touchscreens and Control Panels: Protects display backlights and logic power supplies.
Communication Interfaces: Both internal (EtherCAT, CAN bus) and external (USB, Ethernet) communication ports of the robot require PPTC to prevent port damage caused by hot-plugging and wiring errors.
Key Considerations for Selecting the Right PPTC for Robotics
Hold Current: For motor protection, the hold current must be greater than the motor's peak operating current (e.g., starting current) but must be significantly less than the motor's stall current. Careful study of the motor specifications and practical measurements are required.
Trip Time: Must be fast enough to act before the motor or driver suffers permanent damage (typically within milliseconds to seconds).
PPTC Resistance: In battery-powered robots or those with high energy efficiency requirements, low-resistance PPTC help reduce energy loss and self-heating.
Maximum Voltage and Maximum Current: The bus voltage of servo systems can be relatively high (e.g., 24V, 48V, or even higher). It is essential to ensure the PPTC's rated voltage is sufficient. Its maximum interrupting current must withstand the most severe short-circuit fault current.
Mechanical Strength and Temperature Range: Industrial environments have vibration, requiring PPTC (especially SMD types) to have good solder joint strength. The operating temperature range must cover all robot conditions, from standby to full load operation.
Advantages of PPTC in Robotics Applications
Protects High-Value Assets: Prevents permanent damage to expensive motors, drivers, and sensors due to overcurrent.
Enhances System Resilience: Enables robots to automatically recover from temporary overload faults, greatly improving availability and production efficiency.
Achieves Functional Safety: Helps meet the functional safety goals of robots by preventing fault propagation and ensuring the operation of safety circuits.
Modular Design: Allows for designing independent protection strategies for each joint and each sensor, simplifying system design and fault diagnosis.
Summary:
In modern robot design, the PPTC has evolved from a simple circuit protection component into a key intelligent part for building highly reliable, highly available, and highly safe robotic systems. Like a tireless security guard, it provides real-time protection at multiple critical points such as the robot's power core, sensory nerves, and interaction interfaces, making it an indispensable link in ensuring stable and reliable robot operation.
BHFUSE PPTC with leading advantages such as high current rating, high voltage rating, glue-sealed edges, and ultra-low resistance, have been selected by numerous well-known domestic and international robot manufacturers.